Introduction
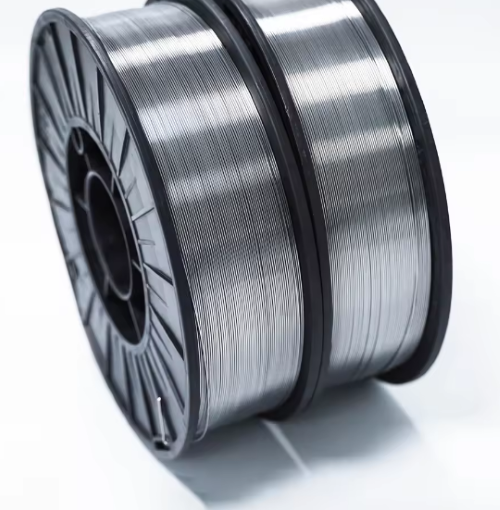
Hafnium, a transition metal known for its high melting point, excellent corrosion resistance, and remarkable ability to absorb neutrons, is a critical material in various advanced technological fields. One of its most useful forms is hafnium wire, which leverages these unique properties to serve a broad spectrum of applications. This article explores ten significant uses of hafnium wire, highlighting its versatility and importance in modern industry and technology.
1. Nuclear Reactors
Hafnium wire is extensively used in nuclear reactors due to its exceptional neutron-absorbing capabilities. It acts as a control rod material, which helps regulate the fission process in nuclear reactors. By adjusting the position of these control rods, operators can control the rate of the nuclear reaction, ensuring safe and efficient energy production.

Related reading: 4 Uses Of Hafnium | The Applications Of Hafnium And Hafnium Alloys
2. Electronics
In the electronics industry, hafnium wire is employed in the manufacture of semiconductors and integrated circuits. Its high thermal stability and resistance to oxidation make it an excellent choice for these applications. Hafnium-based dielectrics, such as hafnium oxide, are used in high-k dielectric materials to improve the performance and efficiency of transistors in advanced microprocessors.

3. Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry benefits from hafnium wire’s high melting point and strength at elevated temperatures. It is used in high-temperature environments, such as in the construction of jet engines and spacecraft components. Hafnium’s ability to maintain its structural integrity under extreme conditions makes it an indispensable material for aerospace applications.
4. Medical Field
Hafnium wire finds applications in the medical field, particularly in surgical instruments and medical implants. Its biocompatibility and resistance to corrosion make it suitable for use in the human body. Additionally, hafnium is used in dental applications, providing durable and long-lasting solutions for dental restorations.
5. Chemical Industry
In the chemical industry, hafnium wire is used as a component in various chemical reactors and equipment that operate under harsh conditions. Its resistance to corrosion by acids and alkalis ensures longevity and reliability in these demanding environments. Hafnium’s chemical stability makes it an ideal material for components exposed to reactive chemicals.
6. Superalloys
Hafnium wire is a crucial additive in the production of superalloys. These alloys are used in high-stress environments, such as in turbine blades for power generation and jet engines. Hafnium enhances the mechanical properties of superalloys, improving their high-temperature strength, creep resistance, and overall durability.
7. Thin Film Deposition
Hafnium wire is utilized in thin film deposition processes, including physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). These processes are essential for creating thin films and coatings used in various industries, such as optics, electronics, and materials science. Hafnium’s excellent adhesion and stability make it a preferred material for these applications.
8. Lighting Industry
In the lighting industry, hafnium wire is used in high-intensity discharge (HID) lamps and other advanced lighting technologies. Its high melting point and electrical conductivity make it suitable for use in environments where conventional materials would fail. Hafnium wire helps improve the efficiency and lifespan of lighting components.
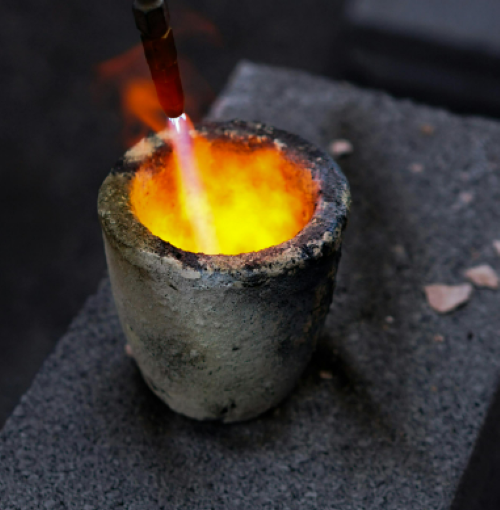
9. Welding
Hafnium wire is employed in welding applications, particularly in tungsten-inert gas (TIG) welding. It serves as an electrode material, providing a stable and consistent arc for high-precision welding tasks. Hafnium’s ability to withstand high temperatures without degrading ensures high-quality welds in various metals and alloys.

Related reading: Electrode Materials for Plasma Cutting Machines
10. Research and Development
Hafnium wire is a valuable material in research and development (R&D) settings, particularly in the fields of materials science and engineering. Its unique properties enable researchers to explore new applications and develop innovative technologies. Hafnium’s versatility and performance under extreme conditions make it an essential tool in cutting-edge scientific investigations.
Conclusion
Hafnium wire plays a crucial role in diverse industries, from nuclear energy and electronics to aerospace and medicine. Its high melting point, excellent corrosion resistance, and neutron-absorbing capabilities make it an invaluable material for a wide range of applications.
As technology continues to advance, the demand for hafnium wire is expected to grow, driving further innovation and expanding its utility in new and exciting ways. The versatility and importance of hafnium wire underscore its significance as a material of the future, contributing to advancements in various fields and supporting the development of next-generation technologies. For more metals and alloys, please check Advanced Refractory Metals (ARM).