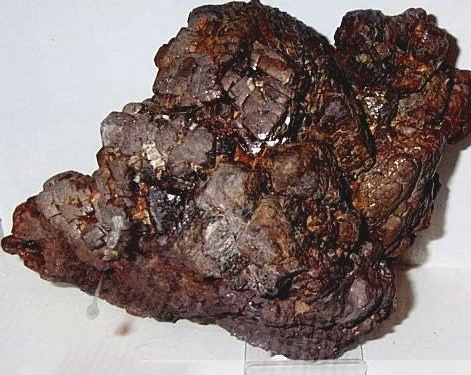
What is Zircon?
Zircon (also known as zircon) is zirconium orthosilicate with a chemical formula of ZrSiO4, which is the most common type of zirconium-containing mineral. Zircon is mainly used as a raw material for zirconate refractory bricks, and can also be used for precision casting sand and ceramic utensils.
What is Zircon Beneficiation?
Zircon beneficiation refers to the process of removing impurities in zircon ore and increasing the content of zircon. Most of the zircon deposits are coastal placers. In the heavy sand containing zircon, there are usually heavy minerals such as magnetite, ilmenite, rutile, and monazite. Generally, when zircon is selected, these heavy minerals are also recovered as target minerals.
What are Zircon Beneficiation Methods?
Zircon beneficiation methods mainly include gravity separation, magnetic separation, electrostatic separation, and flotation.
Gravity separation
Zircon mostly occurs in ilmenite and is often accompanied by heavy minerals such as hematite, chromite, and garnet. Therefore, in the initial stage of enriching zircon, gravity separation is often used, such as using a shaking table to separate heavy minerals from gangue (quartz, feldspar, biotite), etc., and then using other beneficiation methods to separate them from other heavy minerals.
Flotation
The commonly used collectors in this method are fatty acids (oleic acid, sodium oleate), etc.; the slurry conditioner is sodium carbonate; the inhibitor is sodium silicate; the activator is sodium sulfide and heavy metal salts (zirconium chloride, ferric chloride) ); this method also uses oxalic acid to adjust the pulp to acidity and uses amine collectors for flotation.
Electric selection
Conductive minerals such as ilmenite, hematite, chromite, cassiterite, and rutile are separated from non-conductive minerals such as zircon, monazite, garnet, and apatite by utilizing the difference in mineral conductivity. Desliming, grading, drying, and dosing should be done in advance before electrification.
Magnetic separation
Magnetic minerals in heavy minerals include ilmenite, hematite, chromite, garnet, biotite, monazite, etc. Zircon is a non-magnetic mineral or a weak magnetic mineral (the iron in zircon in some deposits is weak magnetic). Magnetic separation is divided into dry and wet. In dry magnetic separation, the selected materials need to be heated, dried, and classified before they can be sorted. The wet type strong magnetic field magnetic separator has a wide separation particle size, and the lower limit of particle size can reach 20um. Therefore, it is more appropriate to use a wet magnetic separator when the zircon particle size is fine.
Wrap up
Since there are many associated minerals in zircon ore, gravity separation, magnetic separation, flotation, electric separation, and other methods should be used in combination. For more information, please visit https://www.samaterials.com/70-zirconium.html.