As the most important type of advanced ceramics, zirconia ceramic material is an important basic material for the development of the modern high-tech industry. Zirconia is widely used in the market, and its specific applications include the solid fuel cell, automobile exhaust treatment, dental materials, ceramic cutting tools, and zirconia fiber core plug.
However, as mobile 5G era approaches at any time, zirconia ceramics become the hot spot of the industry again due to its characteristics such as warm feeling, anti-scratch and wear resistance, no signal shielding, and excellent heat dissipation performance.
Zirconia is insoluble in water, sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and nitric acid. It is slightly soluble in hydrofluoric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid when heated. Pure zirconia is an insulator at room temperature. Adding a stabilizer can increase its conductivity and show ionic conductivity at high temperatures. There are three crystal types of zirconia. The crystal parameters and the schematic diagram of the structure of the three crystal types are shown below.
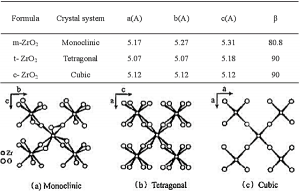
Zirconia ceramics have high hardness, wear resistance, high-temperature thermal stability and impact resistance. The preparation of high-performance zirconia ceramics depends on high-quality zirconia powder and optimized sintering process parameters.
Preparation of high-quality zirconia powder
The preparation methods of high-quality zirconia powder mainly include the physical method and the chemical method. The physical methods include high-temperature spray pyrolysis, spray induction coupled plasma pyrolysis and freeze-drying; chemical methods include gas phase, liquid phase, and solid-phase method. Among them, the liquid phase synthesis method has high efficiency, fine powder particle quality, and simple equipment, so it has been widely used.

The sintering method
Sintering process parameters include sintering temperature, sintering pressure and sintering time. Ceramic materials with very different microstructures and properties can be obtained when the same ceramic materials adopt different sintering processes. At present, the sintering process of zirconia ceramics at home and abroad has pressureless sintering, hot pressing sintering, hot isostatic sintering, and discharge plasma sintering. Pressureless sintering, also known as traditional atmospheric sintering, is the sintering of a prefabricated ceramic body under atmospheric pressure and high-temperature conditions; hot press sintering is a sintering method for applying axial pressure to the powder in the mold; spark plasma sintering (SPS), also known as plasma-activated sintering, is a new rapid sintering technology.
Stanford Advanced Materials supplies high-quality zirconia powder and related products to meet our customers’ R&D and production needs. Please visit http://www.samaterials.com for more information.
