Introduction
Zirconium titanium alloys represent a significant advancement in the field of medical materials, combining the desirable properties of both zirconium and titanium to offer superior biocompatibility and mechanical strength. These alloys have found a wide range of applications in medical devices, implants, and prosthetics, revolutionizing patient care with their durability and compatibility with human tissue.
Biocompatibility
One of the most critical considerations for any material used in medical applications is its biocompatibility.
Zirconium titanium alloys excel in this regard, exhibiting excellent compatibility with human body tissues and fluids. This minimizes the risk of adverse reactions, such as inflammation or rejection, ensuring that implants and devices made from this alloy can be safely incorporated into the body for long-term applications.
Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of zirconium titanium alloys, including their strength, durability, and resistance to wear, make them ideal for use in load-bearing implants such as hip and knee replacements.
These alloys can withstand the repetitive stress and strain associated with daily movements, providing patients with reliable and long-lasting solutions to mobility issues. Additionally, the alloy’s good fracture toughness reduces the risk of implant failure under stress.
Applications in Medical Devices and Implants
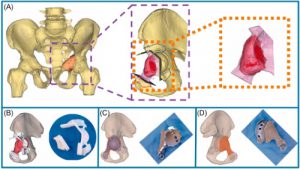
- Orthopedic Implants: Zirconium titanium alloys are widely used in orthopedic implants, including joint replacements and bone screws. Their strength and biocompatibility support the body’s load and promote osseointegration, where bone tissue grows around the implant, securing it in place.
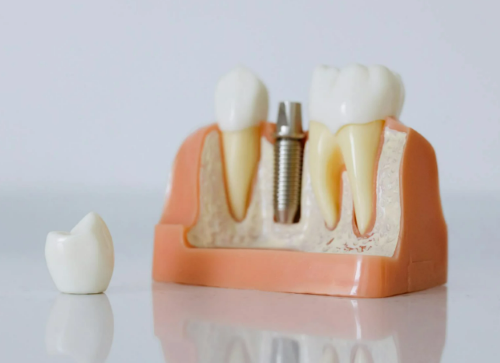
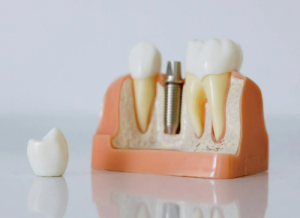
- Dental Implants: In dental applications, the alloy’s resistance to corrosion and mechanical stability make it an excellent choice for dental implants, offering a durable foundation for artificial teeth.
- Cardiovascular Devices: The corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of zirconium titanium alloys are beneficial in cardiovascular devices, such as stents and pacemaker cases, which require long-term stability and minimal interaction with body tissues.
- Surgical Instruments: The alloy’s strength and corrosion resistance also make it suitable for surgical instruments, providing surgeons with reliable tools that maintain their integrity over time.
Advancements and Future Directions
Ongoing research into zirconium titanium alloys aims to further enhance their properties through alloying and surface treatments, improving their performance in biomedical applications.
- Innovations such as nanostructured surfaces and coatings are being explored to increase osseointegration for implants and reduce bacterial adhesion, minimizing the risk of infections.
- The development of zirconium titanium alloys with tailored mechanical properties for specific applications, such as flexible stents or highly durable joint replacements, is another area of active research.
These advancements promise to expand the use of these alloys in the medical field, offering new solutions to complex healthcare challenges.
Conclusion
Zirconium titanium alloys stand at the forefront of biomedical materials, offering an optimal combination of biocompatibility and mechanical properties that make them indispensable in modern medical applications. From enhancing the longevity and reliability of implants to supporting the development of advanced medical devices, these alloys contribute significantly to improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Table 1. Biomedical Applications of Zirconium Titanium Alloys
| Aspect | Details |
| Properties | Compatible with human tissues; ideal for implants due to durability and fracture toughness. |
| Medical Applications | Used in orthopedic and dental implants, cardiovascular devices, and surgical tools. |
| Future Directions | Focus on enhancing alloy properties for better integration and infection resistance. |
As research continues to unveil new possibilities, the role of zirconium titanium alloys in medicine is set to grow, marking a promising future for their application in healthcare. Advanced Refractory Metals (ARM) is a trusted supplier of zirconium titanium alloys. We provide a wide range of zirconium metal products with competitive prices and great delivery time. For more information, please check our homepage.